Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) in Women: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment

Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) is a common viral infection that affects many people worldwide.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for HSV is important, especially for women who may experience unique challenges and considerations related to the virus.
Symptoms
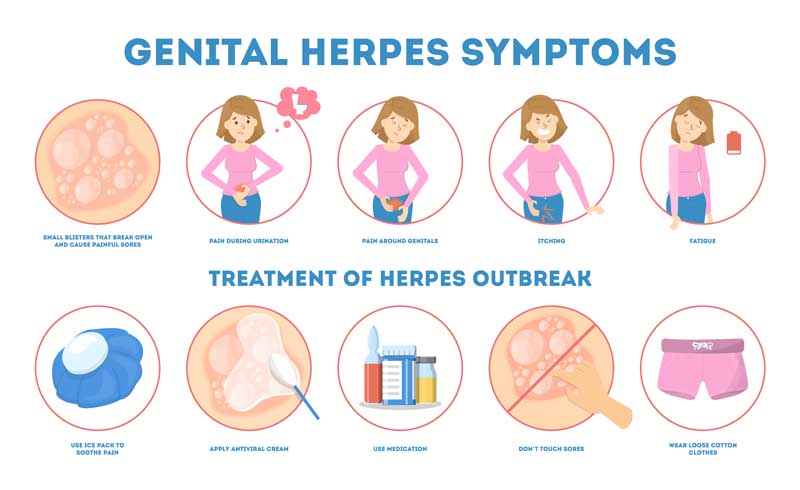
1. Initial Symptoms:
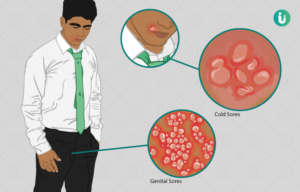
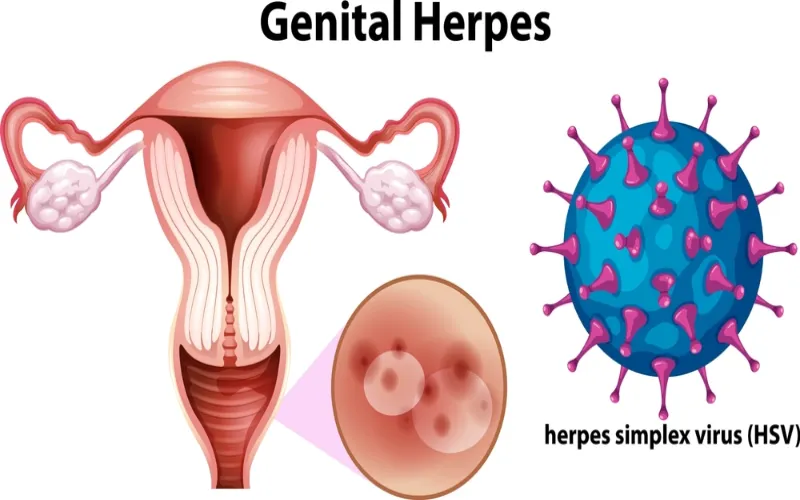
- Blisters and Sores: Painful blisters or sores around the genital area, buttocks, and thighs.
- Itching or Tingling: Many women experience itching or tingling sensations in the affected area before blisters appear.
- Flu-like Symptoms: Fever, body aches, swollen lymph nodes, and fatigue.
2. Recurrent Symptoms:
- Milder Blisters: Recurrent outbreaks are less severe than the initial episode.
- Prodrome Phase: Tingling or itching may occur before an outbreak.
- Less Frequent Over Time: The frequency of outbreaks may decrease over time.
3. Other Symptoms:
- Painful Urination: Due to sores or inflammation around the urethra.
- Vaginal Discharge: An increase in vaginal discharge may occur.
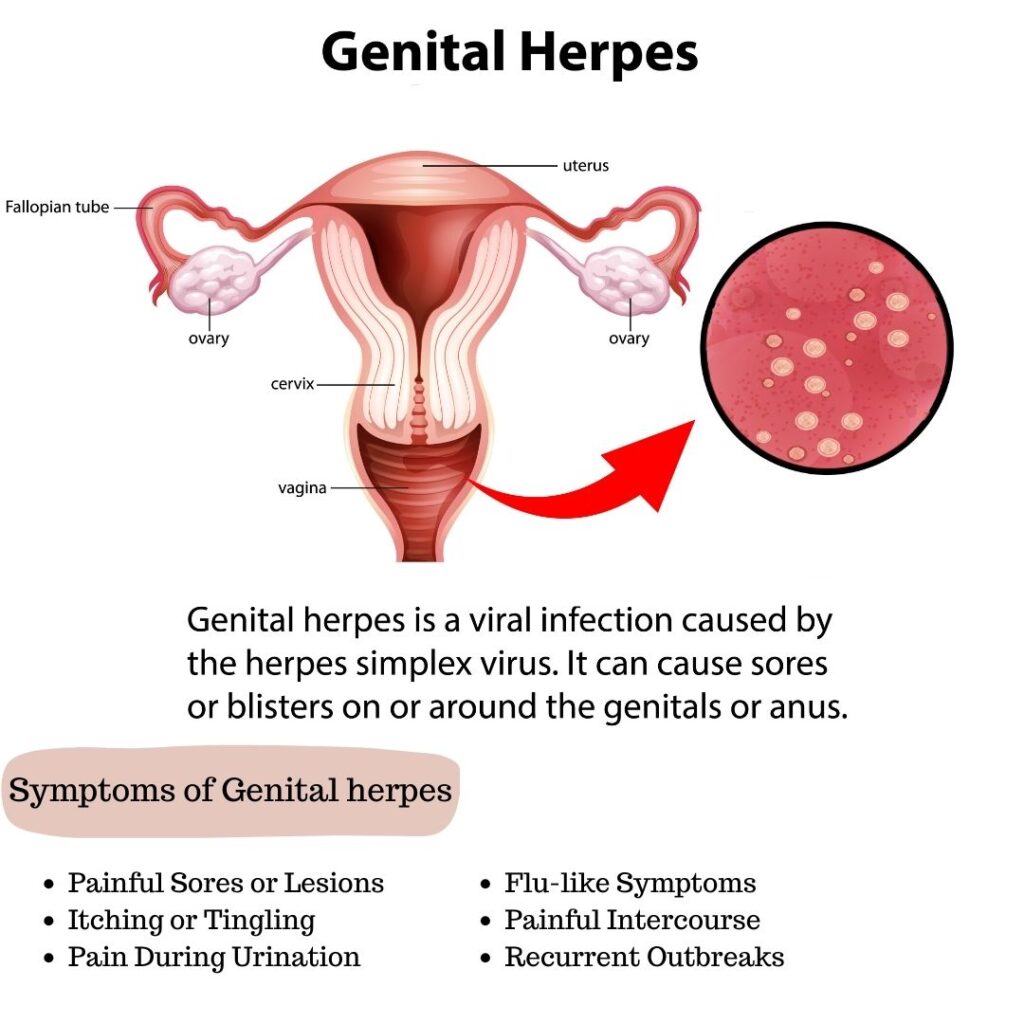
Causes
1. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1):
- Traditionally associated with oral herpes but can cause genital herpes through oral-genital contact.
2. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2):
- Primarily responsible for genital herpes.
- Transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person.
3. Risk Factors:
- Sexual Activity: Engaging in unprotected sex or having multiple partners increases risk.
- Immunocompromised Individuals: Weakened immune systems can make individuals more susceptible.
- History of STIs: Previous sexually transmitted infections can increase vulnerability.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider may examine visible sores.
- Viral Culture: Swabbing a sore and testing for the virus.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Test: Detects HSV DNA in blood, fluid, or tissue samples.
- Blood Tests: Identifies antibodies against HSV, indicating past exposure.

Treatment
1. Antiviral Medications:
- Acyclovir (Zovirax): Helps reduce the severity and frequency of outbreaks.
- Valacyclovir (Valtrex): Often used for long-term management and suppression.
- Famciclovir (Famvir): Another option for antiviral therapy.
2. Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes:
- Warm Baths: Can alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Loose Clothing: Wearing loose-fitting clothing can reduce irritation.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress can help minimize outbreaks.
3. Preventive Measures:
- Condom Use: Reduces the risk of transmission during sexual activity.
- Avoiding Sexual Contact During Outbreaks: Helps prevent spreading the virus.
- Disclosure to Partners: Important for informed consent and prevention.
Pregnancy Considerations
- Risk of Transmission: Pregnant women with HSV can transmit the virus to their baby during childbirth.
- Antiviral Medication May be recommended during pregnancy to reduce the risk of an outbreak during delivery.
- Cesarean Delivery: May be considered if active lesions are present during labor.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
- Counseling and Support Groups: Can help manage emotional distress and provide coping strategies.
- Education: Understanding the condition can reduce stigma and promote healthy relationships.
Conclusion
Proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments can effectively manage the herpes simplex virus in women. Understanding the symptoms and causes is crucial for early diagnosis and transmission prevention.
While there is no cure for HSV, antiviral medications and preventive measures can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected.
Regular communication with healthcare providers is essential for personalized care and management.