Chlamydia in Women: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention

Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and poses significant health risks, especially for women.
Caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, it is often asymptomatic, which can lead to severe complications if left untreated.
This article focuses on Chlamydia in women, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Causes of Chlamydia
Chlamydia is caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, a gram-negative bacterium. It is transmitted primarily through unprotected sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
The bacterium infects the mucous membranes of the cervix, urethra, and rectum. It can also be passed from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth, potentially causing eye infections or pneumonia in newborns.
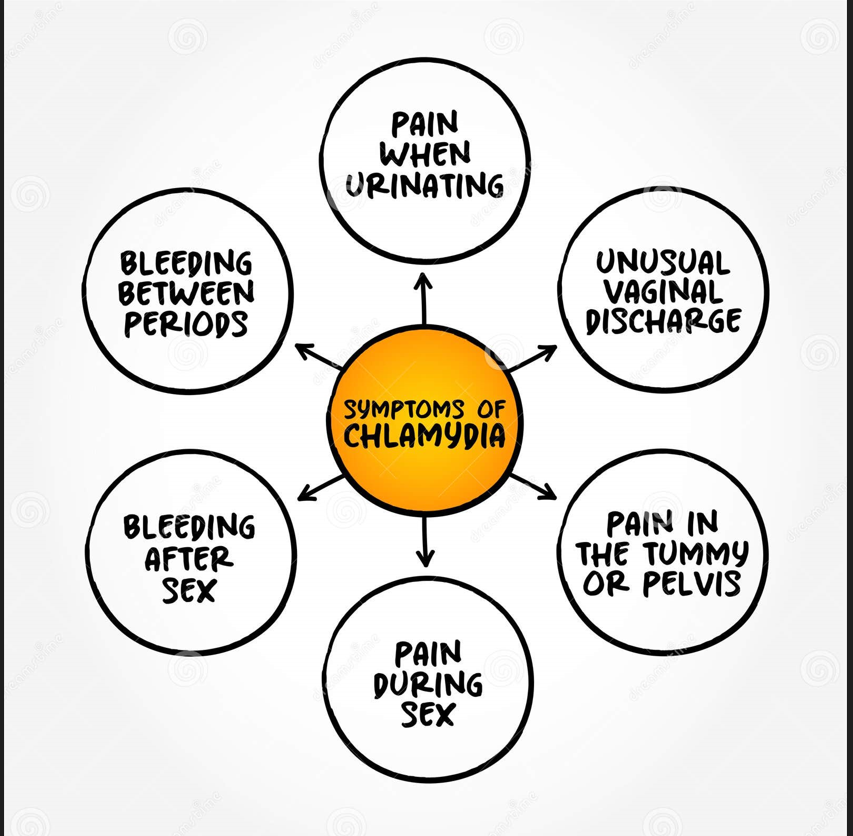
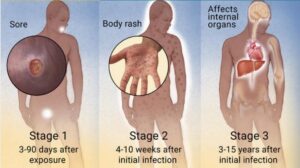
Chlamydia Symptoms in Women
Chlamydia is often referred to as a “silent” infection because many women do not exhibit symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they can be mild or mistaken for other conditions. Symptoms may include:
- Abnormal Vaginal Discharge: The discharge may be thin, watery, or have an unusual odor. It is often more noticeable when it is heavier or changes in color.
- Painful Urination: A burning sensation or discomfort during urination.
- Pelvic Pain: Persistent or intermittent pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area. This pain can be dull or sharp and may occur during or after intercourse.
- Abnormal Bleeding: Spotting or bleeding between menstrual periods or after sexual activity.
- Pain During Intercourse: Discomfort or pain during sexual activity, which may be due to inflammation of the cervix or pelvic organs.
- Vaginal Itching or Irritation: Itching, redness, or swelling of the vaginal area.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Chlamydia in women involves several steps to ensure accurate detection and appropriate treatment:
- Clinical Evaluation: A healthcare provider will review symptoms, conduct a physical examination, and perform a pelvic exam to check for signs of infection.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs): The most accurate tests for Chlamydia, NAATs detect the genetic material of Chlamydia trachomatis. They can be performed using urine samples or swabs from the cervix or vagina.
- Direct Fluorescent Antibody (DFA) Tests: These tests detect chlamydial antigens in cervical or vaginal samples.
- Enzyme Immunoassays (EIAs): These tests identify chlamydial antigens or antibodies.
- Testing for Co-infections: Women with Chlamydia are at higher risk of other STIs. Testing for co-infections, such as gonorrhea, HIV, or syphilis, is often recommended.
Treatment
Chlamydia is effectively treated with antibiotics. The choice of medication and duration of treatment depend on the specific situation:
- First-Line Treatments:
- Azithromycin: A single dose of 1 gram, often preferred for convenience and effectiveness.
- Doxycycline: 100 mg taken orally twice a day for seven days. This option may be used if azithromycin is not suitable.
- Alternative Treatments:
- Erythromycin: Used as an alternative for those who cannot take azithromycin.
- Ofloxacin or Levofloxacin: Considered in cases where other treatments are not appropriate.
- Follow-Up:
- Test of Cure: A follow-up test may be recommended for pregnant women with complicated infections to ensure the infection is completely cleared.
- Re-testing: Women should be re-tested approximately three months after treatment to ensure the infection has not recurred.
- Partner Notification and Treatment: Sexual partners should also be tested and treated to prevent re-infection and further spread of the disease.

Prevention
Preventing Chlamydia involves several strategies to reduce the risk of infection:
- Condom Use: Consistent and correct use of condoms during sexual activity significantly lowers the risk of Chlamydia transmission.
- Regular STI Screening: Sexually active Women, especially those with multiple partners, should undergo regular STI screenings. Early detection and treatment can prevent complications.
- Communication: Open discussions with sexual partners about STI status and sexual health are crucial. It’s important to inform partners if diagnosed with Chlamydia.
- Reducing Risky Behaviors: Limiting the number of sexual partners and avoiding unprotected sex reduces the risk of contracting Chlamydia and other STIs.
- Vaccination: While there is no vaccine specifically for Chlamydia, vaccines are available for other STIs like HPV, which can help reduce overall STI risk.
Complications
If left untreated, Chlamydia can lead to severe health complications for women:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): A serious complication that involves inflammation of the pelvic organs. PID can cause chronic pelvic pain, infertility, and ectopic pregnancy.
- Infertility: Damage to the fallopian tubes from untreated Chlamydia can result in difficulty becoming pregnant.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: An abnormal pregnancy that occurs outside the uterus, often in a fallopian tube, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
- Increased Risk of HIV: Women with Chlamydia are at a higher risk of contracting HIV if exposed.
Conclusion
Chlamydia is a prevalent STI that can have serious health consequences for women if not detected and treated promptly.
Understanding its symptoms, seeking timely diagnosis, adhering to prescribed treatments, and practicing preventive measures are essential for managing and reducing the spread of this infection.
Regular screenings, safe sexual practices, and open communication about sexual health are vital components in protecting overall well-being and preventing complications associated with Chlamydia.
If you suspect you may have Chlamydia or are at risk, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate testing and treatment.