Fostering Connections: Exploring the Importance of Child Social Health
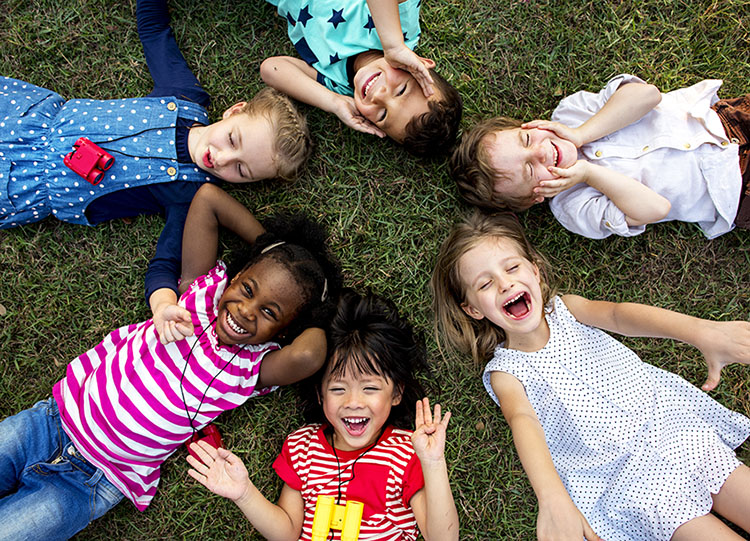

Group of kindergarten kids lying on the grass at park and relax with smiling
Child social health plays a pivotal role in shaping a child’s development, influencing their relationships, self-esteem, and overall well-being. From the earliest interactions with caregivers to navigating friendships and social dynamics in school, fostering healthy social skills and relationships is crucial for a child’s growth. This article delves into the significance of child social health, its components, challenges, and effective strategies for promoting positive social interactions and emotional intelligence.
Importance of Child Social Health
Social health encompasses a child’s ability to interact effectively with others, form meaningful relationships, and navigate social situations with empathy and confidence. Key reasons why social health is vital include:
- Relationship Building: Developing social skills early promotes positive relationships with peers, caregivers, and authority figures, fostering a sense of belonging and support.
- Emotional Intelligence: Social interactions teach children to understand and manage their emotions, empathize with others’ feelings, and communicate effectively.
- Academic Success: Strong social skills correlate with better classroom behavior, cooperation, and engagement in learning activities, contributing to academic achievement.
- Conflict Resolution: Learning to resolve conflicts peacefully and negotiate differences builds resilience and enhances problem-solving abilities.
Components of Child Social Health
Child social health comprises various interconnected components that contribute to overall social competence:
- Social Skills: Abilities such as communication, active listening, sharing, taking turns, and cooperating form the foundation for positive interactions.
- Empathy: Understanding and responding to others’ emotions fosters compassion, kindness, and supportive relationships.
- Peer Relationships: Forming friendships, navigating group dynamics, and developing peer acceptance are crucial for social integration and emotional well-being.
- Self-Expression: Encouraging children to express themselves authentically and assertively contributes to self-confidence and self-advocacy.
- Respect for Diversity: Appreciating differences in cultures, beliefs, and perspectives promotes inclusivity and reduces prejudice and discrimination.
Promoting Child Social Health
Parents, caregivers, educators, and communities play essential roles in nurturing child social health. Here are effective strategies to support healthy social development:
- Model Positive Social Behaviors: Demonstrate empathy, respect, and effective communication in interactions with children and others.
- Encourage Play and Peer Interaction: Provide opportunities for unstructured play, group activities, and cooperative games that foster social skills and teamwork.
- Teach Social Skills: Use role-playing, storytelling, and games to teach children how to introduce themselves, join conversations, and resolve conflicts peacefully.
- Promote Inclusive Environments: Create settings where diversity is celebrated, and all children feel valued and respected for who they are.
- Facilitate Emotional Expression: Encourage children to talk about their feelings, validate their emotions, and teach them appropriate ways to express and manage emotions.
- Build Empathy: Discuss different perspectives, read books about diverse experiences, and engage in activities that promote understanding of others’ feelings and needs.
- Support Peer Relationships: Monitor social interactions, intervene when necessary to promote positive behavior, and teach skills for making and maintaining friendships.
Challenges and Considerations
While promoting child social health is crucial, several challenges may impact social development:
- Social Isolation: Factors such as moving homes, changing schools, or limited access to social activities can affect opportunities for social interaction.
- Bullying and Peer Pressure: Negative social experiences, including bullying and peer pressure, can undermine self-esteem and social confidence.
- Technology Use: Excessive screen time and social media can impact face-to-face interactions and contribute to cyberbullying and social comparison.
- Developmental Differences: Children develop social skills at different rates, requiring tailored support and understanding of individual needs.
Conclusion
Investing in child social health is essential for nurturing well-rounded, confident, and empathetic individuals capable of thriving in diverse social environments. By prioritizing social skills development, fostering inclusive environments, and promoting positive relationships, caregivers and educators can empower children to navigate social challenges with resilience and empathy.
In essence, promoting child social health is not only about teaching manners and etiquette but about cultivating meaningful connections, fostering empathy, and equipping children with essential life skills. By embracing diversity, supporting peer relationships, and teaching conflict resolution, we pave the way for a future generation that values collaboration, respects differences, and contributes positively to their communities.
By fostering a supportive social environment grounded in understanding and respect, we enable children to build lasting friendships, communicate effectively, and navigate social complexities with confidence and compassion.