Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) in Men: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) is a common viral infection that can affect both men and women. However, its manifestations and implications can differ between genders.
This article delves into the specifics of HSV in men, including its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and preventive measures.
What is Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)?
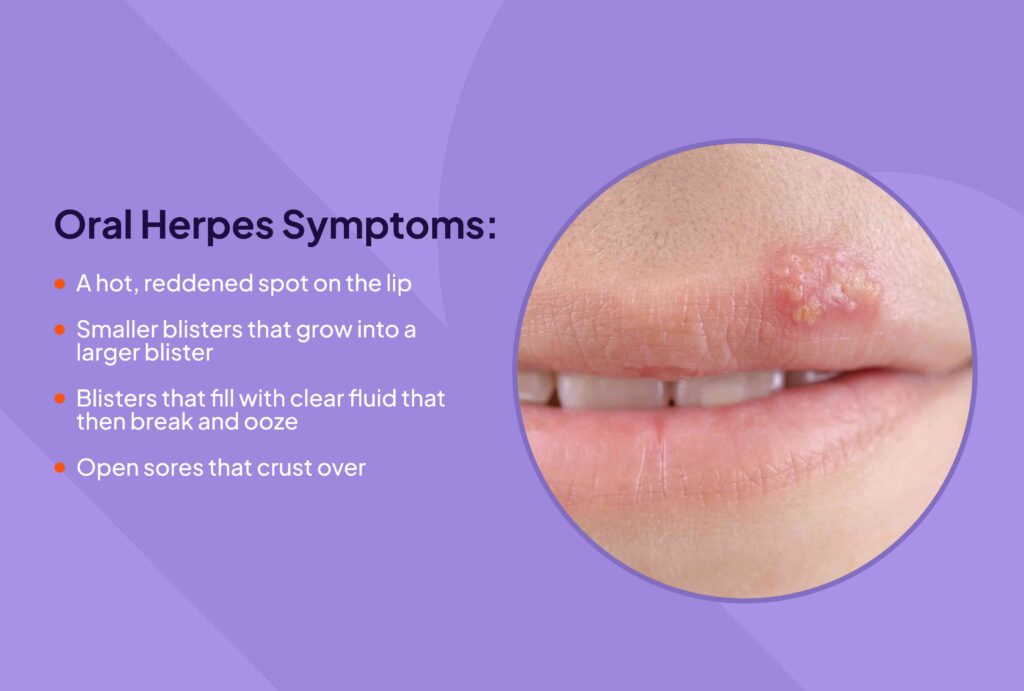
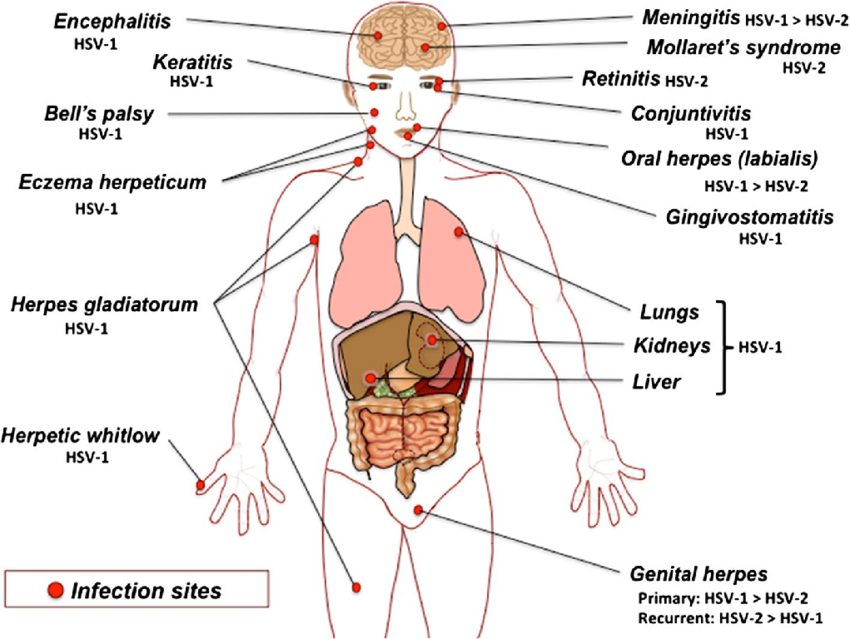
HSV is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus, which has two forms: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 typically causes oral herpes, which is cold sores around the mouth.
HSV-2 primarily causes genital herpes, affecting the genital and anal areas. However, both types can cause infections in either location.
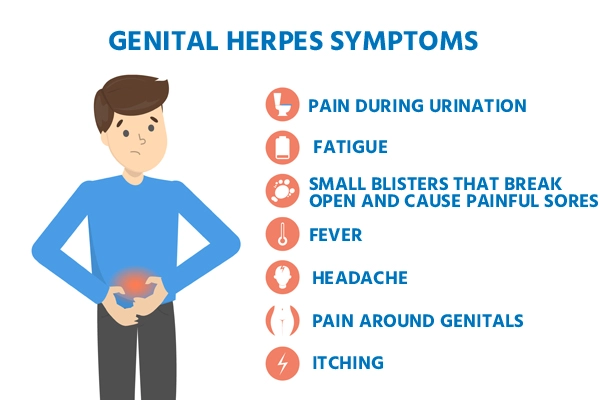
Symptoms of HSV in Men
The symptoms of HSV in men can vary, with some individuals experiencing severe outbreaks and others remaining asymptomatic. The common symptoms include:
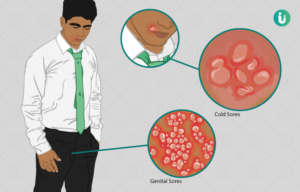
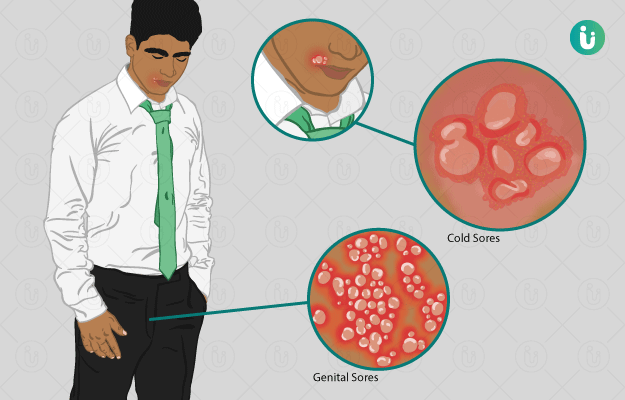
- Blisters and Sores: Painful blisters or sores on the penis, scrotum, buttocks, anus, or thighs. These can break open and ooze fluid before forming scabs and healing.
- Pain and Itching: Itching, tingling, or burning sensations in the infected areas.
- Flu-like Symptoms: Fever, headache, muscle aches, and swollen lymph nodes, especially during the first outbreak.
- Difficulty Urinating: Sores can sometimes cause pain and discomfort during urination.
Causes and Transmission
HSV is primarily spread through direct contact with an infected person. This can occur during:
- Sexual Contact: HSV-2 is mainly transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has the virus.
- Skin-to-Skin Contact: HSV-1 can be spread through kissing or sharing items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Asymptomatic Shedding: The virus can be transmitted even with no visible symptoms through viral shedding.
Diagnosis of HSV
Diagnosis of HSV in men involves several methods:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider may diagnose HSV based on the appearance of sores.
- Viral Culture: Swabbing a fresh sore to test for the virus.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Test: Detects HSV DNA from a swab sample.
- Blood Tests: Detect antibodies to HSV, indicating a past or current infection.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for HSV, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and reducing the frequency of outbreaks:
- Antiviral Medications: Drugs such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can alleviate discomfort.
- Topical Creams: Creams to soothe itching and pain from sores.

Preventive Measures
Preventing the spread of HSV involves several strategies:
- Use of Condoms: While not foolproof, condoms can reduce the risk of transmission.
- Avoiding Sexual Activity During Outbreaks: Refrain from sexual contact when symptoms are present.
- Regular Testing: Routine STD testing helps in early detection and management.
- Disclosure to Partners: Inform sexual partners so they can take appropriate precautions about the infection.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
HSV can also have a significant psychological impact due to the stigma associated with sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Men diagnosed with HSV might experience feelings of shame, guilt, or anxiety. Support from healthcare providers, counseling, and support groups can be crucial in managing these emotional challenges.
Conclusion
Herpes Simplex Virus in men is manageable with the proper treatment and preventive measures. Awareness and education are vital in reducing transmission and coping with the infection.
If you suspect you have HSV or have been diagnosed with it, consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the best management strategies for your situation.