Syphilis in Women: Diagnosing, and Preventing a Silent Threat
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum.
While it affects both men and women, its impact on women can be particularly severe, often leading to complications during pregnancy and significant health issues if left untreated.
This article provides an in-depth look at syphilis in women, exploring its causes, symptoms, stages, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What is Syphilis?
Syphilis is a bacterial infection typically spread through sexual contact. The disease progresses through distinct stages, each with its symptoms.
Without treatment, syphilis can lead to serious health problems, including damage to the heart, brain, and other organs.
Causes of Syphilis
Syphilis is caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, which can enter the body through minor cuts or abrasions in the skin or mucous membranes.
The most common mode of transmission is through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. It can also be transmitted from a pregnant woman to her baby, leading to congenital syphilis.
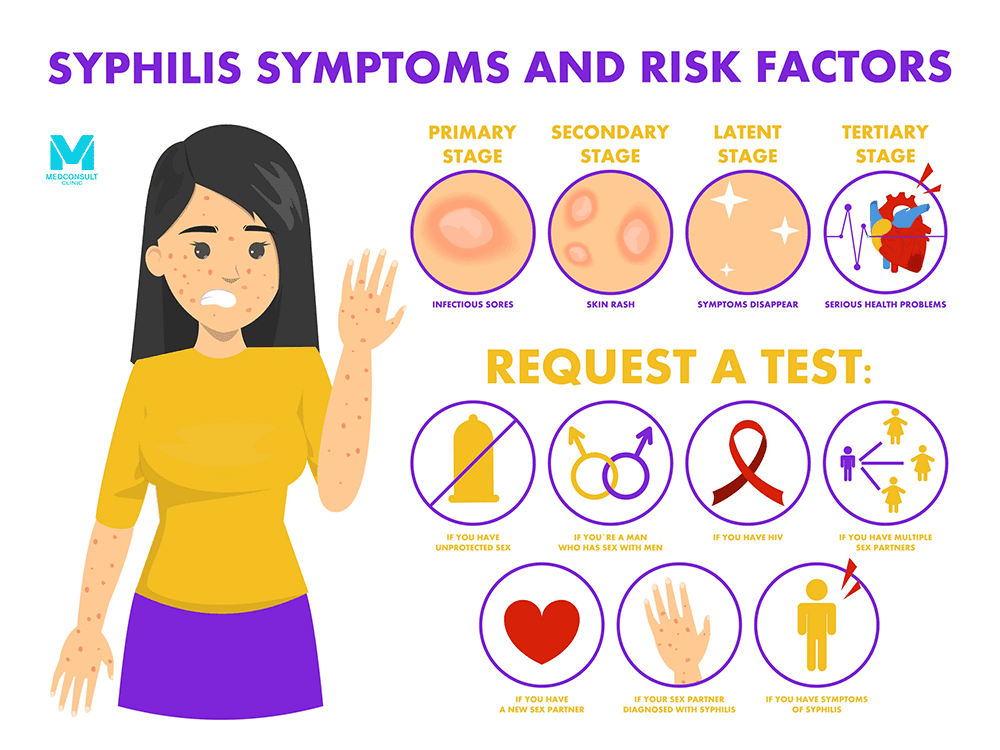
Symptoms of Syphilis in Women
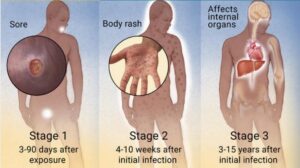
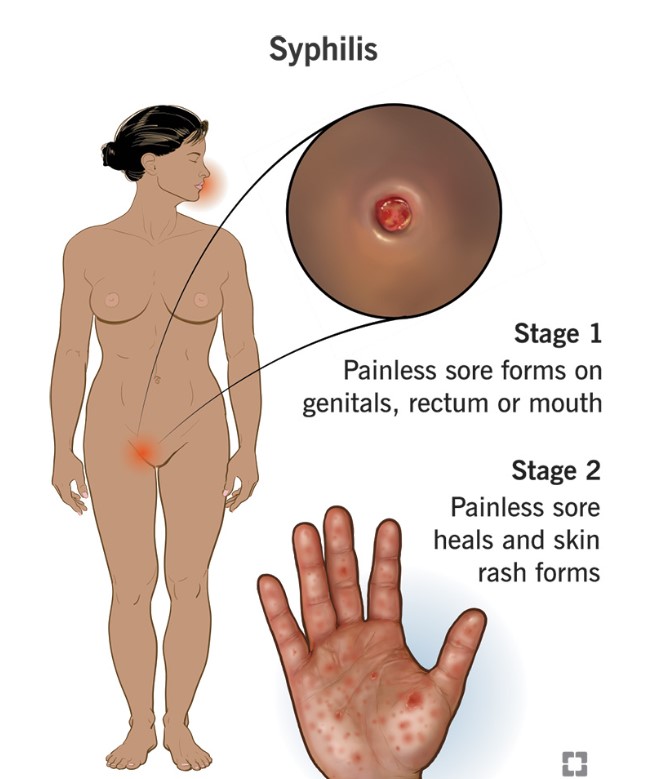
Primary Stage
- Chancre: The first sign is usually a small, painless sore (chancre) at the site of infection, typically the genitals, anus, or mouth.
- This sore appears about three weeks after exposure and heals within three to six weeks.
Secondary Stage
- Skin Rash: A rash may develop, often on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. It may not be itchy, but it can be widespread.
- Flu-like Symptoms: Fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, and muscle aches are common.
- Mucous Membrane Lesions: Sores in the mouth, vagina, or anus.
Latent Stage
- No Symptoms: The infection enters a dormant phase, lasting for years. Despite the lack of symptoms, the bacteria remain in the body and can cause serious damage.
Tertiary Stage
- Severe Health Issues: Without treatment, syphilis can damage the heart, brain, nerves, eyes, blood vessels, liver, bones, and joints. Symptoms can include paralysis, blindness, dementia, and even death.
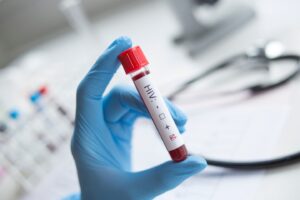
Diagnosis of Syphilis
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Syphilis can be diagnosed through:
- Blood Tests: Detect the body’s antibodies in response to the infection.
- Physical Examination: Identification of sores or rashes.
- Lumbar Puncture: A spinal tap may be performed in cases of suspected nervous system involvement.
Treatment of Syphilis
Syphilis is treatable, especially in its early stages. The primary treatment is antibiotics:
- Penicillin: The most effective treatment. A single injection can cure early-stage syphilis.
- Alternative Antibiotics: Other antibiotics like doxycycline or azithromycin may be used for those allergic to penicillin.
Treatment not only cures the infection but also prevents further damage and transmission.
Prevention of Syphilis
Preventing syphilis involves practising safe sex and taking proactive health measures:
- Condom Use: Consistent and correct use of condoms can significantly reduce the risk of transmission.
- Regular Testing: Regular STI screenings, especially for sexually active women, can help detect and treat syphilis early.
- Partner Communication: Open communication with sexual partners about STI testing and prevention.
- Prenatal Care: Pregnant women should receive syphilis screening to prevent congenital syphilis.
Importance of Awareness and Education
Raising awareness about syphilis and promoting education on safe sexual practices are essential in combating this infection.
Understanding the risks, symptoms, and the importance of early diagnosis can help reduce the prevalence of syphilis and its complications.
Conclusion
Syphilis in women is a serious health issue that requires prompt attention and treatment.
By understanding the symptoms, stages, and prevention methods, women can take proactive steps to protect their health and that of their partners.
Regular screenings and safe sexual practices are vital in the fight against syphilis, ensuring a healthier future for all.
For further information on syphilis and other STIs, consult your healthcare provider or visit reputable health websites.
Early detection and treatment are key to overcoming syphilis and maintaining good health.