Understanding and Nurturing Child Behavioral Health
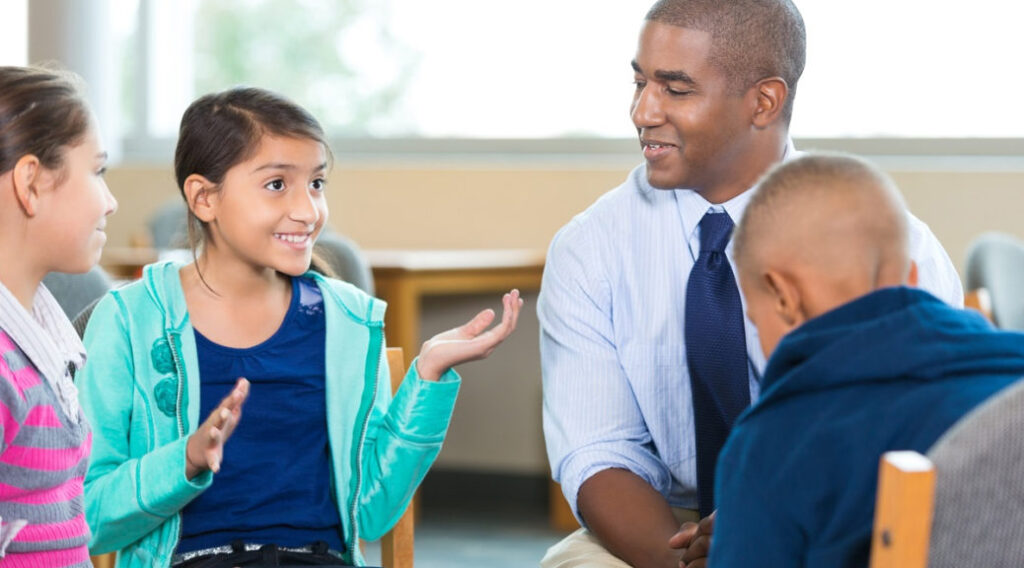

Diverse group of elementary age little girls and little boys are sitting in circle with mid adult African American male counselor or therapist. Mental health professional is leading children's group therapy session. Children are smiling and talking expressively.
Child behavioral health encompasses the complex interplay of behaviors, emotions, and social interactions that influence a child’s well-being and development. From infancy through adolescence, children navigate various stages of behavioral growth and encounter challenges that shape their personalities and interactions with the world. This article explores the importance of child behavioral health, its components, challenges, and strategies for promoting positive behaviors and emotional resilience.
Importance of Child Behavioral Health
Behavioral health is integral to a child’s overall development and impacts multiple aspects of their life:
- Academic Achievement: Positive behaviors such as attentiveness, self-discipline, and cooperation contribute to better academic performance and classroom engagement.
- Social Relationships: Behaviors like empathy, sharing, and conflict resolution skills facilitate positive interactions with peers, caregivers, and authority figures.
- Emotional Regulation: Managing emotions effectively promotes resilience, reduces stress, and enhances coping mechanisms during challenging situations.
- Long-Term Well-Being: Early intervention and support for behavioral health issues can prevent the development of more serious emotional or behavioral disorders in adulthood.
Components of Child Behavioral Health
Child behavioral health encompasses a range of behaviors and emotional responses that influence their daily interactions and development:
- Emotional Regulation: The ability to identify, understand, and manage emotions constructively is crucial for adaptive behaviors and social interactions.
- Behavioral Self-Control: Skills such as impulse control, patience, and following rules contribute to positive behavior management and decision-making.
- Social Skills: Interpersonal skills like communication, listening, empathy, and cooperation facilitate healthy relationships and social integration.
- Attention and Focus: Developing attention span, concentration, and task persistence supports learning, academic success, and self-directed activities.
- Problem-Solving Abilities: Cognitive skills for problem-solving, decision-making, and critical thinking promote autonomy and adaptive behaviors.
Promoting Child Behavioral Health
Effective strategies for promoting positive behavioral health in children involve collaboration among parents, caregivers, educators, and healthcare providers:
- Establish Clear Expectations: Set consistent and age-appropriate rules, routines, and expectations to provide structure and predictability for children.
- Teach and Model Positive Behaviors: Demonstrate desired behaviors such as kindness, respect, and responsibility in daily interactions with children.
- Encourage Emotional Expression: Create a safe environment for children to express their feelings and emotions openly. Validate their experiences and teach constructive ways to manage emotions.
- Provide Opportunities for Social Learning: Facilitate peer interactions, group activities, and cooperative play to enhance social skills and teamwork.
- Use Positive Reinforcement: Acknowledge and praise desirable behaviors to reinforce positive actions and motivate children to continue practicing them.
- Teach Problem-Solving Skills: Guide children in identifying problems, exploring solutions, and making decisions independently. Encourage critical thinking and creativity.
- Address Underlying Issues: Identify and address any underlying factors contributing to behavioral challenges, such as learning disabilities, trauma, or environmental stressors.
Challenges and Considerations
While promoting child behavioral health is crucial, several challenges may impact behavioral development:
- Developmental Variability: Children develop at different rates and may exhibit behaviors that require understanding and individualized support.
- Environmental Factors: Home environment, peer influences, socioeconomic status, and community resources can impact behavioral health outcomes.
- Co-occurring Conditions: Behavioral issues may coexist with mental health disorders, learning disabilities, or medical conditions that require comprehensive assessment and intervention.
- Cultural and Societal Influences: Cultural norms, beliefs, and societal expectations can influence behavioral expectations and responses to behavioral challenges.
Conclusion
Investing in child behavioral health is essential for nurturing resilient, empathetic, and socially competent individuals who can navigate life’s challenges with confidence. By promoting emotional regulation, teaching social skills, reinforcing positive behaviors, and addressing underlying issues, caregivers and educators can support children in developing healthy behavioral patterns.
In essence, fostering positive behavioral health is about creating a nurturing environment that promotes self-awareness, empathy, and effective communication. By understanding the complexities of child behavior and providing consistent support and guidance, we empower children to thrive academically, socially, and emotionally.
By prioritizing early intervention, promoting resilience, and fostering a supportive community, we equip children with the tools they need to build positive relationships, make responsible choices, and achieve their full potential in all aspects of life.